Symptoms of bunion: What should you know?
Index
Bunions are a common deformity that affects the big toe joint. This disorder can cause a variety of symptoms and discomfort, limiting mobility and affecting quality of life. Identifying bunionette symptoms early is critical to addressing the condition appropriately. This article will explore the characteristics, symptoms, causes and treatment options for bunions.
Characteristics of bunions
Understanding the characteristics of bunions is critical to identifying and managing this condition. Their definitions and typical formations are detailed below.
What is a Bunion?
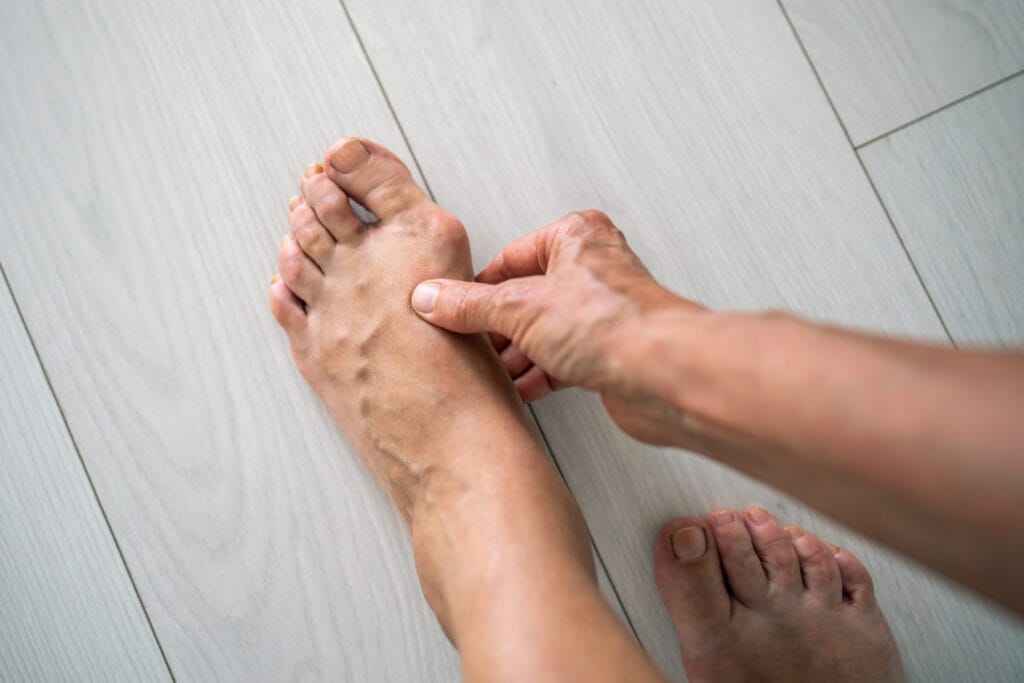
A bunion, medically known as hallux valgus, is defined as a deformity that affects the joint of the big toe. This condition causes the toe to move toward the other toes, creating a bony protrusion at the base of the toe. This protrusion can be visible and is often painful, especially when wearing shoes that put pressure on the affected area.
How do you form a Bunion?
The formation of a bunion occurs through a series of biomechanical changes in the bones and joints of the foot. This process can be influenced by genetic factors, such as inheritance of a predisposed bony anatomy, and by the use of inappropriate footwear. The typical steps in the development of this deformity are described below:
- Misalignment of the first metatarsal: As the first metatarsal moves outward, the big toe tends to tilt inward.
- Increased pressure on the joint: This deviation creates excessive pressure on the metatarsophalangeal joint, leading to swelling and development of the bump.
- Bone tissue development: Additional bone tissue forms in response to stress, resulting in the characteristic prominence of the bunion.
Alterations in the normal function of the foot, combined with the frequent use of narrow-toed or high-heeled shoes, can accelerate this process. Over time, the bunion can cause not only aesthetic but also functional changes, affecting mobility and walking comfort.
Common Symptoms of Bunions
Bunions can present a variety of symptoms that affect the quality of life of those who suffer from them. The following is a description of the most common bunion symptoms and manifestations associated with this condition.
Pain and Discomfort
The sensation of pain is one of the most characteristic symptoms. This discomfort may be continuous or appear intermittently. The pain is usually intensified by wearing shoes that do not offer adequate support or by maintaining pressure on the affected joint. Many people report pain that is localized at the base of the big toe, although it may radiate throughout the foot. The intensity of the pain can vary from mild discomfort to a sharp pain that makes daily activities such as walking or standing difficult.
Bone protrusion
A visible protrusion at the big toe joint is the most obvious feature of a bunion. This bony deformity can be felt and is usually noticeable when looking at the foot. Over time, the bump may increase in size, causing not only an aesthetic change, but also a functional change. The way the big toe bends toward the other toes is critical in identifying the presence of this condition.
Redness and Inflammation
Swelling in the region of the bunion is a common symptom. The skin overlying the bump may become red and warm to the touch. This inflammatory reaction is a consequence of the constant pressure exerted on the joint, which can cause additional pain. In many cases, the inflammation can also trigger sensitivity to friction, making it even more difficult to choose appropriate footwear.
Limited Mobility
The range of motion of the big toe may be restricted due to stiffness in the affected joint. This limitation can interfere with the ability to move the toe normally, affecting balance and walking. Over time, the lack of mobility can cause people to alter their gait patterns, which may contribute to other foot and leg problems.
Causes and Risk Factors
The development of bunions can be attributed to a combination of factors. The causes can be both hereditary and environmental, and understanding them is essential to addressing this condition in depth.
Genetic Predisposition
One of the most significant causes in the formation of bunions is genetic predisposition. Heredity plays a crucial role, as many people have a family history of this deformity. The structural characteristics of the foot can be transmitted from generation to generation, which increases the probability of developing bunions. Thus, individuals with family members who have this condition are more likely to experience it as well.
Inappropriate Footwear
The type of footwear worn has a considerable impact on the development of bunions. Wearing tight, narrow-toed or very high shoes can result in excessive pressure on the big toe. This abnormal pressure alters the normal alignment of the foot and can accentuate bunion formation. For this reason, it is essential to select footwear that provides proper support and improves foot comfort.
Biomechanical Factors
Biomechanical factors also contribute to this condition. People who have an abnormal shape in their foot structure may be more at risk. For example, conditions such as low or high arches can influence how weight is distributed when walking. Repeated stress on the joints of the foot can result in gradual misalignment, encouraging the development of bunions.
Associated Medical Conditions
There are certain medical conditions that can facilitate the development of bunions. Some of these include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis, which causes inflammation in the joints.
- Neuromuscular diseases affecting balance and coordination.
- Alterations in rhythm and weight distribution during gait.
These conditions can impair foot health and contribute to the development of deformities, including bunions. It is important to take these factors into account in order to establish effective prevention and proper diagnosis if associated symptoms appear.
Diagnosis of bunions
Diagnosis of bunions is a crucial process to assess the severity of the condition. This includes a detailed visual examination and, if necessary, additional tests to confirm the presence of bunion symptoms and to rule out other pathologies. The following are the techniques used to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Physical Examination
The physical examination is the first step in the diagnosis of bunions. During this evaluation, the physician will perform a series of observations and tests. Generally, this process includes:
- A visual inspection of the foot to identify deformity and signs of inflammation.
- Palpation of the affected area to assess the pain and tenderness of the joint.
- Mobility tests to determine the flexibility of the big toe and metatarsophalangeal joint.
Based on this evaluation, the specialist will be able to determine the presence of a bunion and its degree of severity. It is common to ask questions about the patient’s medical history, as well as previous discomfort or similar symptoms.
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests are considered necessary to obtain a clearer view of the deformity and to rule out other bone or joint problems. The most commonly used techniques are:
- X-ray: The X-ray of the foot allows us to see the alignment of the bones, the degree of deformity of the bunion and any damage to nearby joints.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Although not as common, MRI may be used if soft tissue damage or other underlying problems are suspected.
These tests are essential to create an appropriate treatment plan and ensure that the patient receives the correct care based on the severity of his or her condition.
Treatment Options
Treatment of bunions can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the symptoms the patient presents with. There are both conservative approaches and surgical options that can be considered to improve quality of life.
Conservative Approaches
Conservative treatments are the first line of defense in the management of bunions. They are usually less invasive and can provide significant symptom relief.
Change of Footwear
Proper footwear is crucial. Shoes should be chosen that are wide, with good support and without high heels to avoid pressure on the bunion. Avoiding narrow-toed shoes is essential to allow proper alignment of the toes.
Orthopedic Inoles
Custom orthotic Inoles can help redistribute pressure in the foot and improve alignment. These devices not only relieve pain but can also prevent the progression of deformity and improve foot function.
Pain Medication
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly used to relieve pain and inflammation in the affected area. These medications offer temporary relief and can be an effective option to combat episodes of severe discomfort.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy can be a key element in the treatment of bunions. A physical therapist can design a customized plan that includes exercises to strengthen and improve foot flexibility. These exercises help maintain function and may reduce long-term pain.
Surgical Treatments
When conservative approaches do not provide adequate relief, surgical treatments may be an option to consider.
Bunionectomy
This procedure is one of the most common and involves the removal of the protruding part of the bone. It also involves realignment of the big toe to restore its correct position. Bunionectomy can be very effective, especially in severe cases.
Osteotomy
In osteotomy, the metatarsal bones are cut and realigned. This approach seeks to correct the posture of the toe, thus relieving pressure on the affected joint. This type of surgery may be necessary in situations where the deformity has advanced significantly.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Determining the right time to seek medical attention is critical to the effective management of any foot pain or discomfort. Although some symptoms may be manageable, there are signs that indicate urgent professional evaluation is required.
Symptoms Requiring Evaluation
Several symptoms may signal the need to consult a specialist, especially if they occur continuously or worsen over time. The most significant include:
- Persistent Pain: If discomfort in the big toe is constant and affects quality of life.
- Difficulty Finding Shoes: Recurrent inability to wear comfortable shoes due to the bunion should be cause for consultation.
- Significant Swelling: Severe swelling and redness in the joint may indicate problems that need medical attention.
- Reduced Mobility: Limitations in the movement of the big toe that affect balance or gait should be evaluated.
- Callus development: The appearance of calluses on the foot generated by friction may be a sign of an underlying problem that requires attention.
Preparation for Medical Consultation
Before going for a consultation, it is advisable to be adequately prepared. Effective preparation can facilitate diagnosis and treatment. Here are some steps to follow:
- Document Symptoms: Note the intensity of the pain, the frequency of episodes and any factors that worsen or relieve it.
- Medical History: Gather information on family history of bunions, use of footwear and other relevant medical conditions.
- Consult the Primary Care Physician: Many times, it is helpful to begin the process by consulting the primary care physician to obtain a referral to a specialist.
- Prepare Questions: It is advisable to prepare a list of questions to discuss during the consultation, thus ensuring that all necessary information is addressed.
Prevention of bunions
Prevention of bunions is key to maintaining podiatric health. Adopting good daily practices can reduce the risk of developing this deformity, ensuring comfort and functionality in the feet.
Choice of Footwear
The type of footwear plays a key role in the prevention of bunions. It is crucial to opt for shoes that offer good support and do not compress the feet. Some aspects to consider include:
- Wide shoes: Choose shoes with enough room in the toe box to allow toes to be placed naturally without pressure.
- Avoid High Heels: High heels can aggravate pressure on the big toe, favoring the formation of bunions.
- Flexible Materials: Opt for materials that adapt to the foot, avoiding those that are too rigid or that rub against the affected part.
- Adequate Support: Look for shoes that provide good arch support and keep the foot properly aligned.
Foot Exercises
Performing specific exercises can help strengthen foot muscles and improve flexibility, which helps prevent bunions. Some effective exercise options include:
- Toe Stretches: Involves stretching and moving the toes to improve their mobility and alignment.
- Roll a Ball: Placing your foot on a tennis ball and rolling it gently can help relieve tension and improve circulation.
- Arches on the Floor: Performing movements to form arches on the floor with the toes can strengthen the muscles of the bottom of the foot.
- Point Lifting: Attempting to pick up small balls or towels with the toes strengthens the intrinsic muscles of the foot.
Smou Insoles: Specializing in Orthopedic Insole Specialty Store
At Smou we are specialists in the design and manufacture of orthopedic Inoles adapted to different foot needs. If you are looking for bunion insoles, we have the Smou Hallux model, an insole specifically developed to relieve pain and improve alignment in cases of hallux valgus. Its design limits flexion of the big toe and reduces pressure on the joint, offering more stability and comfort with every step.
In addition, in our store you will find other effective orthopedic Inoles to treat pathologies such as plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, metatarsalgia or flat feet. All our Inoles have been designed based on the clinical experience of orthopedic specialists, combining high quality materials with a structure that favors a healthy footprint.
We invite you to visit our online store to discover all the available options and find the most suitable Insole for you. If you have any questions, we will be happy to advise you.
Did you like this content? Share it on your social networks:

